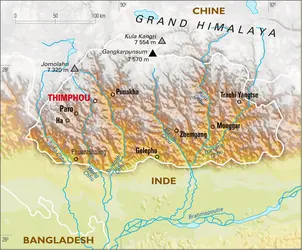
BHOUTAN
| Nom officiel | Royaume du Bhoutan (BT) |
| Chef de l'État | Le roi Jigme Khesar Wangchuk (depuis le 14 décembre 2006) |
| Chef du gouvernement | Lyonpo Chogyal Dago Rigdzin (par intérim depuis le 1er novembre 2023) |
| Capitale | Thimphou |
| Langue officielle | Dzongkha |
| Unité monétaire | Ngultrum (BTN) 4
|
| Population (estim.) |
770 400 (2023) |
| Superficie |
38 394 km²
|
Bibliographie
Économie et vie politique
M. Aris, Bhutan, the EarlyHistory of a HimalayanKingdom, Aris & Phillips, Warminster (R.-U.), 1979
; Sources for the History of Bhutan, Universität Wien, Vienne, 1986
M. Aris & M. Hutt dir., Bhutan : Aspects of Culture and Development, Kiscadale Publications, Stirlingshire, 1994
V. H. Coelho, Sikkim and Bhutan, State Mutual Book and Periodical Service, New York, 1988
B. S. Das, Mission to Bhutan : a Nation in Transition, Vikas Publication, New Delhi, 1995
Far EasternEconomicReview, numéros hebdomadaires et annuaires, Hong Kong
G. L. Harris, J. A. Giddins, T. E. Lux et al., Area Handbook for Nepal, Bhutan and Sikkim, American Univ. Washington (D.C.), 1973
P. P. Karan, HimalayanKingdoms : Bhutan, Sikkim and Nepal, New York, 1963 ; « Bhoutan », map supplement, in Ann. Ass. of American Geographers, 1965 ; Bhutan. Environment, Culture and DevelopmentStrategy, South Asia Books, Columbia, 1988
R. S. Kharat, Bhutan in SAARC:Role of a Small State in a Regional Alliance, South Asian Publishers, New Delhi, 1999
A. Lamballe, « Le Bhoutan, ou un Royaume bouddhiste dans l'Himalaya », in L'Afrique et l'Asie modernes, Paris, no 122, 3e trim. 1979
T. Mathou, Le Bhoutan, royaume du bonheur national brut : entre mythe et réalité, L’Harmattan, Paris, 2013
H. N. Misra, Bhutan. Problems and Policies, South Asia Books, 1988
Nagendra Singh, Bhutan : aKingdom in the Himalayas, Thomson Press, New Delhi, 1972
E. L. Rose, The Politics of Bhutan, Cornell Univ. Press, Ithaca, Londres, 1977
N. Rustomji, EnchantedFrontiers : Sikkim, Bhutan and India'sNortheasternBorderlands, Oxford Univ. Press, Bombay, 1971
A. C. Sinha, Bhutan:Ethnic Identity and National Dilemma, Reliance Publishing House, New Delhi, 1991
; HimalayanKindgomBhutan: Tradition, Transition and Transformation, Indus Publishing, New Delhi, 2001
R. Verma, India'sRole in the Emergence of Contemporary Bhutan, Delhi, 1988.
Histoire et art
M. Aris, « The Admonition of the thunderbolt canon-ball and its place in the bhutanese new year festival », in Bull. School of Oriental and AfricanStudies, XXXIX, no 3, Londres, 1976 ; Bhutan, the EarlyHistory of a HimalayanKingdom, Aris & Phillips, Warminster, 1979 ; JamyangKhyentse's Brief Discourse on the Essence of the Ways, Kailash, V, no 3, 1977 ; SomeConsiderations on the EarlyHistory of Bhutan, Tibetan Studies, Zurich, 1978 ; Sources for the History of Bhutan, Universität Wien, 1986 ; « The Temple-palace og g Tam-zhing as Described by its Founders », in Arts asiatiques, t. XLIII, pp. 33-39, Paris, 1988
D. Bhattacharya, Bhutan, the HimalayanParadise, Oxford and I.B.H. Publ., New Delhi, 1975
« Bhutan », in Demeures des hommes, sanctuaires des dieux, catal. expos., pp. 498-514, Rome-Paris, 1987
« Le Bhutan », in A. W. Macdonald dir., Les Royaumes de l'Himalaya, pp. 66-115, Imprimerie nationale, Paris, 1982
A. M. Blondeau, Religions du Tibet, histoire des religions, Encyclopédie de la Pléiade, 3, Paris, 1976
N. Das, The Dragon Country, the General History of Bhutan, Orient Longman Ltd., New Delhi, 1974
S. Davis, Remarks on the Religions and Social Institutions of the Bouteas of Boutan, from the Unpublished Journal of the Late Samuel Davis, Transactions of the Royal Asiatic Society, I, 1830
P. T. Denwood, Bhutan and Its Architecture, Objets et Mondes, XIV, no 4, 1974
A. Eden, R. B. Pemberton & W. Griffith, Political Missions to Bootan, Manjusri Bibliotheca Himalaica, New Delhi, rééd. 1972
H. V. Guenther, The Life and Teachings of Naropa, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1963
J. D. Hooker, HimalayanJournals, 2 vol., Londres, 1854
Y. Imaeda, « Peintures cosmiques du Bhutan », in OrientaliaIosephiTucciMemoriaeDicata, pp. 627-634, I.S.M.E.O., Rome, 1987
Y. Imaeda & F. Pommaret, « Le Monastère de g Tamzhing (Tamshing) au Bhutan central », in Arts asiatiques, t. XLII, pp. 19-30, 1987
P. P. Karan, Bhutan,[...]
La suite de cet article est accessible aux abonnés
- Des contenus variés, complets et fiables
- Accessible sur tous les écrans
- Pas de publicité
Déjà abonné ? Se connecter
Écrit par
- Benoît CAILMAIL : conservateur des bibliothèques à la Bibliothèque nationale de France
- François DURAND-DASTÈS : professeur à l'université de Paris-VII-Denis-Diderot
- Alain LAMBALLE : lieutenant-colonel d'infanterie, docteur de troisième cycle en sociologie politique
- Chantal MASSONAUD : chargée de mission au musée Guimet
Classification
Médias
Autres références
-
ASIE (Géographie humaine et régionale) - Dynamiques régionales
- Écrit par Manuelle FRANCK , Bernard HOURCADE , Georges MUTIN , Philippe PELLETIER et Jean-Luc RACINE
- 24 799 mots
- 10 médias
...musulman et bicéphale, dont la partie orientale a fait sécession en 1971 pour devenir le Bangladesh. Au nord, les États himalayens du Népal et du Bhoutan font tampon avec la Chine, qui possède avec l'Inde une frontière commune, toujours contestée tant à l'ouest de l'Himalaya qu'à... -
ISLAM (Histoire) - Le monde musulman contemporain
- Écrit par Françoise AUBIN , Olivier CARRÉ , Nathalie CLAYER , Encyclopædia Universalis , Andrée FEILLARD , Marc GABORIEAU , Altan GOKALP , Denys LOMBARD , Robert MANTRAN , Alexandre POPOVIC , Catherine POUJOL et Jean-Louis TRIAUD
- 31 436 mots
- 12 médias
...Maldives (100 %), Pakistan (97 %), Bangladesh (85 %) ; ils sont en minorité dans l'immense Union indienne (12 %), à Sri Lanka (7 %), au Népal (3 %) et au Bhoutan (3 %). Ils doivent donc s'affirmer non seulement contre l'Occident, mais aussi contre la communauté religieuse dominante, celle des hindous. Ensuite,... -
LEPCHA ou RONG
- Écrit par Yvan BARBÉ
- 451 mots
-
RICHESSE DÉFINITIONS ET MESURES DE LA
- Écrit par Jean GADREY
- 4 791 mots
- 5 médias
...Nations unies. Ils ne permettent pas non plus de traiter les enjeux du développement durable. Bien qu’il s’agisse d’un cas qui semble quelque peu exotique, on mentionnera enfin, en raison de son audience internationale, l’indicateur de « bonheur national brut » (Gross National Happiness Index) du Bhoutan...