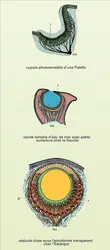
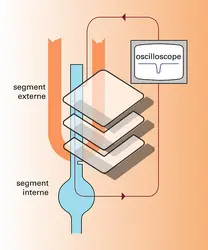
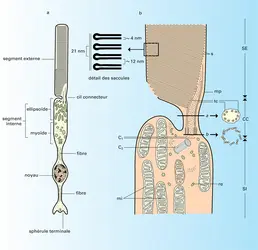
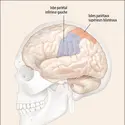
VISION Photoréception rétinienne
Bibliographie
H. B. Barlow, R. M. Hill & W. R. Levick, « Retinal Ganglion cells responding-selectively to direction and speed of image motion in the rabbit », in Journ. Physiol., vol. CLXXIII, 1964
D. A. Baylor & M. G. F. Fuortes, « Electrical Responses of single cones in the retina of the turtle », in Journ. Physiol., vol. CCVII, 1970
D. A. Baylor, T. D. Lamb & K. W. Yau, « The Membrane current of single rod outer segments » et « Responses of retinal rods to single photons », in Journ. Physiol. Lond., vol. CCLXXXVIII, 1979
N. Berardi, S. Bisti, A. Cattaneo, A. Fiorentini & L. Maffei, « Correlation between the preferred orientation and spatial frequency of neurones in visual areas 17 and 18 of the cat », in Journ. Physiol. Lond., vol. CCCXXIII, 1982
H. M. Brown, S. Hagiwara, A. Koike & R. Meech, « Membrane Properties of a barnacle photoreceptor examined by the voltage-clamp technique », in Journ. Physiol. Lond., vol. CCVIII, 1970
H. J. A. Dartnall, J. K. Bowmaker & J. D. Mollon, « Human Visual Pigments : microspectrophotometric results from the eyes of seven persons », in Proc. Royal Soc. Lond. B, vol. CCXX, 1983
E. A. Dratz & P. A. Hargrave, « The Structure of rhodopsin and the rod outer segment disk membrane », in Trends in Bioch. Sci., vol. VIII, 1983
B. Dreher, Y. Fukuda & R. W. Rodieck, « Identification, classification and anatomical segregation of cells with X-like and Y-like properties in the lateral geniculate nucleus of old-world primates », in Journ. Physiol. Lond., vol. CCLVIII, 1976
R. M. Eakin, « Structure of invertebrate photoreceptors », in H. J. A. Dartnall, Handbook of Sensory Physiology, vol. VII, part. 1, New York, 1972
D. H. Hubel, « Exploration of the primary visual cortex, 1955-1978 », in Nature, vol. CCXCIX, 1982
Y. Koutalos & K.-W. Yau, « A Rich Complexity emerges in phototransduction », in Current Opinion in Neurobiology, vol. III, 1993
S. Levay, D. H. Hubel & T. N. Wiesel, « The Pattern of ocular dominance columns in macaque visual cortex revealed by a reduced silver stain », in Journ. Comp. Neurol., vol. CLIX, 1975
M. S. Livingstone & D. H. Hubel, « Anatomy and physiology of a color system in the primate visual cortex », in Journ. Neurosc., vol. IV, 1984
L. Maffei & A. Fiorentini, « Spatial Frequency rows in the striate visual cortex », in Vision Res., vol. XVII, 1977
S. L. Merbs & J. Nathans, « Absorption Spectra of human cone pigments », in Nature, vol. CCCLVI, 1992
F. M. de Monasterio, « Properties of concentrically organized X and Y ganglion cells of macaque retina », in Journ. Neurophysiol., vol. XLI, 1978
J. Nathans, T. P. Piantanida, R. L. Eddy, T. B. Shows & D. Hogness, « Molecular Genetics of inherited variation in human color vision », in Science, vol. CCXXXII, 1986
J. Nathans, D. Thomas & D. S. Hogness, « Molecular Genetics of human color vision : the genes encoding blue, green and red pigment », ibid., 1986
B. J. Nunn, J. L. Schnapf & D. A. Baylor, « Spectral Sensitivity of single cones in the retina of Macaca fascicularis », in Nature, vol. CCCIX, 1984
G. F. Poggio & B. Fischer, « Binocular Interaction and depth sensitivity in striate and prestriate cortex of behaving rhesus monkey », in Journ. Neurophysiol., vol. XL, 1977
E. de Robertis, « Some Observations on the ultrastructure and morphogenesis of photoreceptors », in Journ. Gen. Physiol., vol. XLIII, 1960
L. Stryer, « Visual Excitation and recovery », in Journ. Biol. Chem., vol. CCLXVI, 1991
T. Tomita, « Electrical Activity of vertebrate photoreceptors », in Quart. Rev. Biophysics, vol. III, 1970
R. E. Weller & J. H. Kaas, « The Organization of the visual system in Galago : comparisons with monkeys », in D. E. Haines, The Lesser Bushbaby (Galago) as an Animal Model, Boca Raton, 1982
T. N. Wiesel, « Postnatal[...]
La suite de cet article est accessible aux abonnés
- Des contenus variés, complets et fiables
- Accessible sur tous les écrans
- Pas de publicité
Déjà abonné ? Se connecter
Écrit par
- Yves GALIFRET : professeur émérite à l'université de Paris-VI-Pierre-et-Marie-Curie
Classification
Médias
Autres références
-
AMPHIBIENS ou BATRACIENS
- Écrit par Pierre CLAIRAMBAULT , Philippe JANVIER et Jean-Claude RAGE
- 6 177 mots
- 19 médias
...suffit en effet de comparer une grenouille et un triton). Chez les Gymniophones, l'œil se trouve sous la peau ou même sous la couverture osseuse du crâne. Certains amphibiens, comme le protée ou les Gymniophones, sont aveugles (adaptation à la vie souterraine). La protection de l'œil est assurée par la présence... -
CERVEAU ET GESTES
- Écrit par Didier LE GALL et François OSIURAK
- 916 mots
- 1 média
Les informations visuelles permettent de déterminer la position d’un objet par rapport au corps. Les informations proprioceptives proviennent de capteurs situés au niveau des tendons, des articulations et des muscles. Grâce à ces informations, nous sommes capables à tout moment d’avoir une représentation... -
COGNITIVES SCIENCES
- Écrit par Daniel ANDLER
- 19 265 mots
- 4 médias
Les recherches sur lavision sont peut-être la branche la plus « scientifique » (au sens étroit) des sciences cognitives. C'est aussi celle dans laquelle les neurosciences jouent le plus grand rôle. Le second fait n'explique qu'en partie le premier : la vision présente par rapport à d'autres modalités... -
COULEUR
- Écrit par Pierre FLEURY et Christian IMBERT
- 7 733 mots
- 21 médias
On considère en psychophysiologie, sous les noms de teinte, saturation et luminosité d'une lumière, trois qualités dont chacune dépend principalement de la caractéristique « chromatique » (λd ou p) ou photométrique (L) correspondante, mais parfois aussi quelque peu des deux autres.... - Afficher les 44 références